Image for illustrative purposes
AI-POWERED VPP AND DERM
After the Paris Agreement in 2016, the power sector across the globe began undergoing major changes which are focused on meeting the rising energy demand and curtailing carbon emissions. To meet the increasing energy demand and climate goals, industry is upgrading not only the grid infrastructure but also increasing the share of renewable energy resources. But there is a limit to how much additional grid infrastructure and generation resources (be it renewable or conventional) can be installed. This has forced us to look for other ways and completely rethink how we meet the electricity demand and climate goals, that too in an optimized manner.
Recently, Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) and Distributed Energy Resource Management (DERM) powered by artificial intelligence have emerged as potential solutions. Utilities all over the world, specifically in the advanced economies, are utilizing AI powered VPPs and DERM to optimize the use of renewable energy integrated with the electricity grid and achieve operational goals including economic efficiency, security, and reliability of supply.
AI-Powered Flexibility Services
Electric utilities in advanced economies are readily utilizing AI powered VPPs and DERM to achieve required grid flexibility. These technologies have become tools for the grid operators and utilities which are trying to optimize operations in developed economies.
Virtual Power Plants
VPP is a system of systems which relies on an advanced software platform-based AI-driven predictive models, which can optimally orchestrate the dispatch of distributed energy resources such as wind farms, solar parks, storage units, and flexible controllable loads to a distribution or wholesale market.
VPPs have enabled electricity consumers to participate in the electricity market and act as prosumers of electricity that provide services to the electricity grid while meeting their own needs which was otherwise not be possible. This has been made possible through aggregation of behind the meter DERs for instance solar PV systems, batteries, EVs and demand response potential.
It is interesting to note that VPPs provide control over the distributed energy resources which in turn provide services that are usually drawn from conventional power plants but with a much smaller environmental footprint and land use.
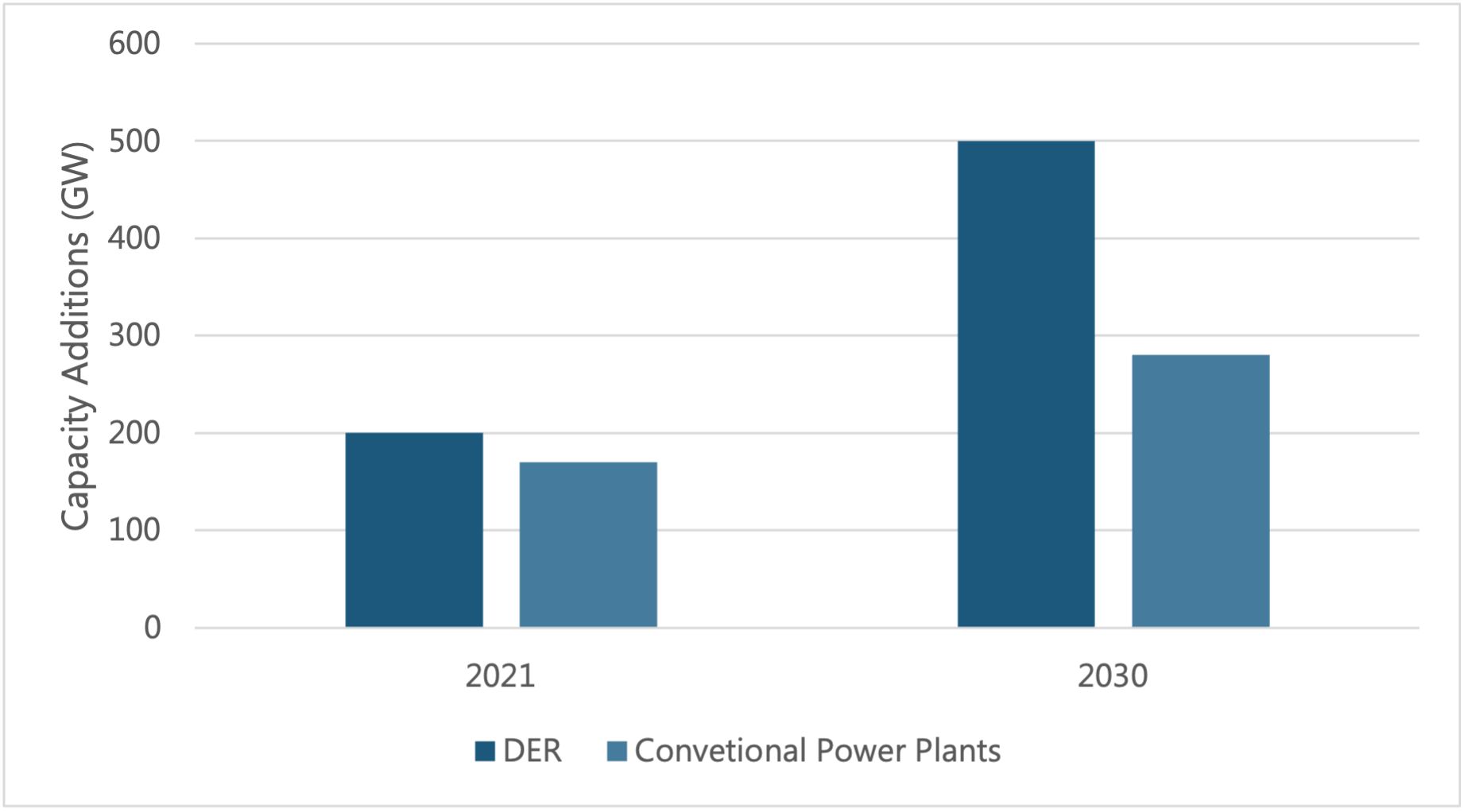
Figure 1: Generation Capacity of DERs versus Conventional Generation.
Source: PTR Inc.
Distributed Energy Resource Management
DERM is essentially a software platform that allows real time control, coordination, and optimization of different types of distributed energy resources, for instance solar, wind and energy storage systems. As per the estimates of PTR, the cumulative annual power injecting capability of DERs for instance utility scale renewables, grid edge services such as rooftop PV solar, battery storage units, electric vehicles, combine heat and power units and controllable smart home appliances have for the very first time surpassed the electric power generation capacity from conventional power plants (thermal and nuclear) worldwide in 2021.
VPPs have enabled electricity consumers to participate in the electricity market and act as prosumers of electricity that provide services to the electricity grid while meeting their own needs which was otherwise not be possible.
Decentralization of the generation assets at this scale, which is only going to increase in coming years, has created several challenges for the grid operators and utilities. Utilities and grid operators in order to cater to the surge in the distributed energy resources require an active power management system. As the majority of the distributed energy resources are not under the control of utilities or grid operators, utilities are under an obligation (under grid code) to supply the power to the consumers while maintaining a balanced DER portfolio.
In order to maintain reliability and stability of the grid, localized active power management of distribution feeders and circuits is required. These features are available in the latest DERMs through which utilities can effectively manage complex power systems and deliver reliable power to consumers.
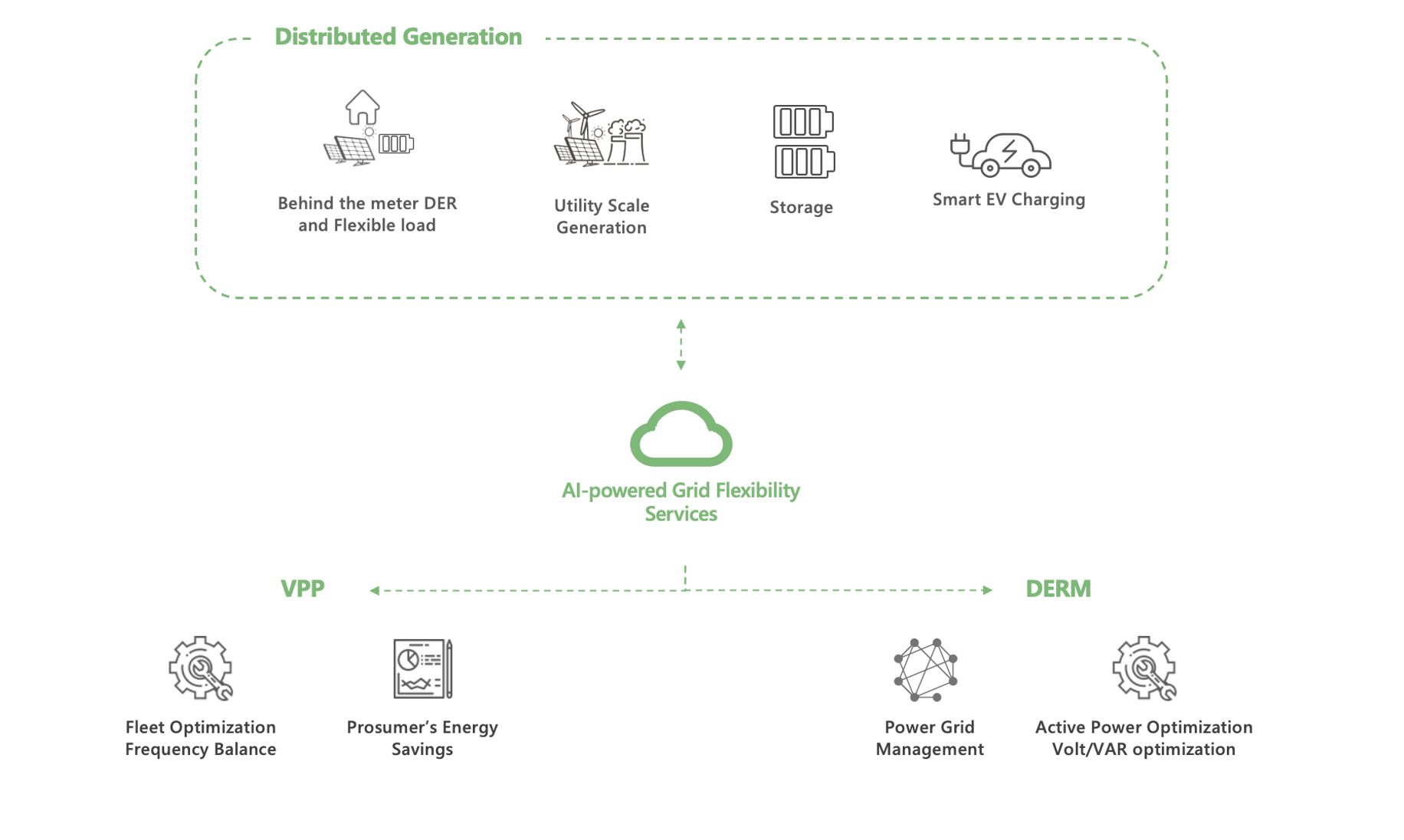
Figure 2: AI-Powered Grid Flexibility Services Assisting Electric Utilities to Optimally Manage Decentralization.
Source: PTR Inc.
Key Global Markets for Grid Flexibility Services
As per the estimates of PTR, Europe is the frontrunner in terms of AI powered grid flexibility services as both the VPP and DERM are gaining traction in the region due to rising share of renewable energy, and grid edge DERs. In this regard, Europe is followed by Australia which is a potential energy market for grid flexibility services mainly due to widespread deployment of grid edge distributed energy resources and high energy per capita consumption.
Europe
Historically, the European VPP and DERM market is mainly driven by the requirement for integration of increasing share of supply-side renewable generation. The expansion in wind power from 94 GW to 197 GW and solar power from 18 GW to 120 GW in the last decade has paved way for grid flexibility services.
In 2021, the European DERM installed capacity accounted for around 50 GW. Within Europe, the UK is the leading market accounting for nearly 14 GW, followed by Germany with nearly 6.5 GW.
On the other hand, Germany is the leading market in terms of installed VPP capacity accounting for nearly 4 GW, followed by the UK with nearly 1 GW of VPP capacity. The majority of the VPP capacity is driven by utility scale solar and wind power deployments in these countries.
It is expected that the UK and Germany will remain the dominant market for both DERM and VPP in Europe till 2030. Grid flexibility capacity of the UK and Germany is anticipated to reach beyond 100 GW by 2030. The main reason behind the maturity of these markets is the increase in the deployment of grid-edge renewables. Furthermore, the regional and national regulations allowing the demand-side flexibility to be part of energy market for energy trading will also result in the increasing capacity of the grid flexibility.
It is expected that the UK and Germany will remain the dominant market for both DERM and VPP in Europe till 2030. Grid flexibility capacity of the UK and Germany is anticipated to reach beyond 100 GW by 2030.
Australia
Australia’s energy per capita consumption is 25% higher than the average of OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) member countries, accounting for nearly 8,930 kWh. Higher energy per capita consumption has created an opportunity for flexible loads to act as key grid flexibility assets via VPPs.
The Australian power sector is becoming more decentralized due to the growing share of renewable energy generation which is expected to be 45% of Australia’s total electricity generation by 2050 up from 12% in 2021. A major portion of this renewable energy generation target is planned to be achieved by installing rooftop solar and residential energy storage battery units projected to account for 124 GW and 126 GWh by 2050. In line with the highest rooftop solar generation capacity and projected massive deployment of residential storage solutions, Australia stands out as a market for the VPP and DERM with significant potential.
With the ongoing expansion of solar rooftop and residential battery storage across all the states, Australia is right on its way to becoming one of the global leaders in terms of VPP deployment in the coming years. Australia is estimated to have nearly 9 GW of DERM and 7 GW of VPP capacity by 2030. The majority of the demand will be driven by the states including Victoria and Queensland.
The Vitoria’s energy company, Origin, plans to achieve a VPP capacity of 2 GW in the coming four years, the major portion of the VPP will be coming from residential storage and solar rooftop. In addition, Transgrid and Ergon Energy Networks are also planning to build VPP aggregation platforms in Southern Australia and Queensland, respectively. The VPP programs will enable the utilities to optimally manage the dispatch of renewable energy resources.
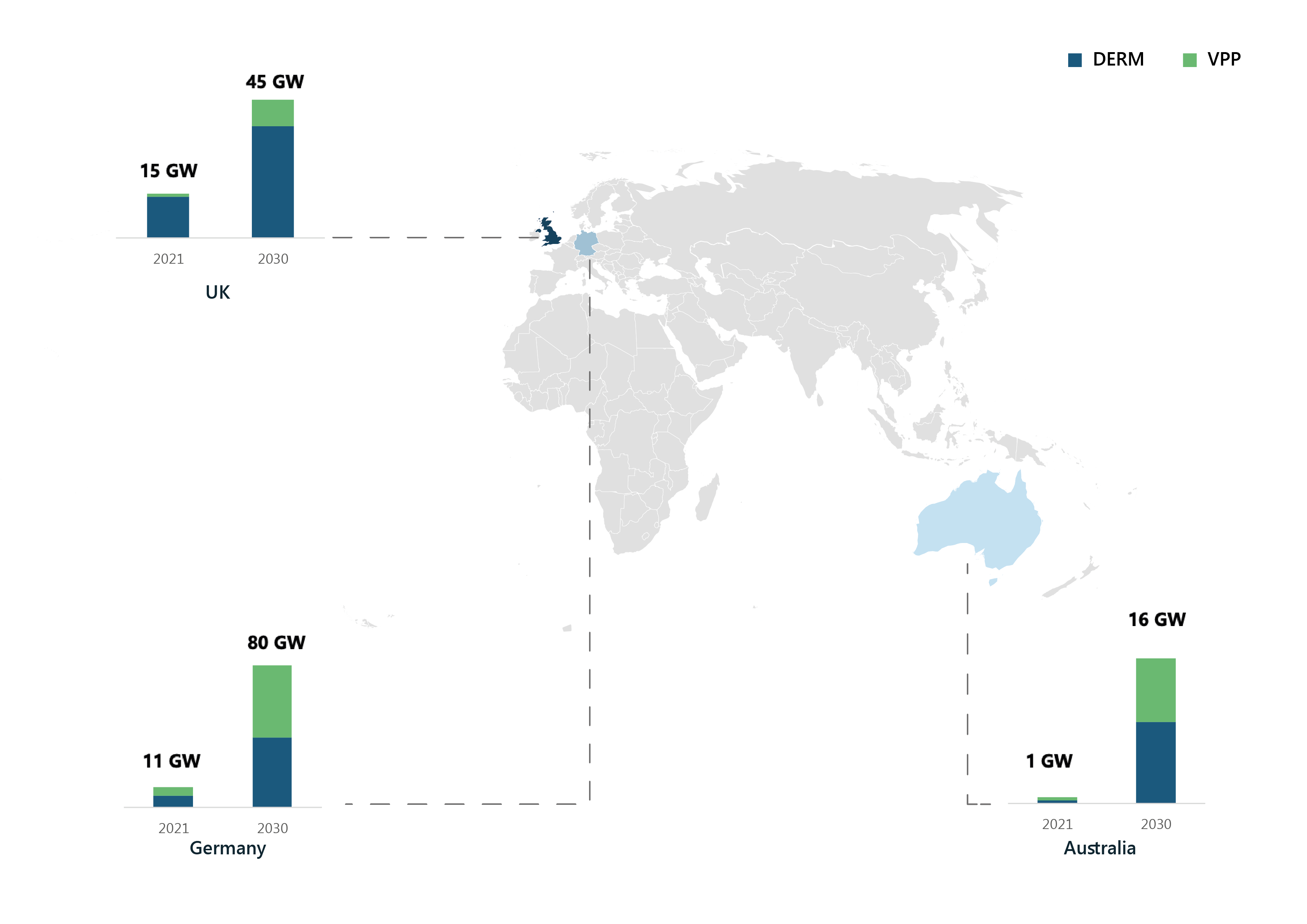
Figure 3: Grid Flexibility Capacity in Key European Markets and Australia (2021-2030)
Source: PTR Inc.
Looking Ahead
PTR has observed that Europe and Australia are leading the way in terms of adoption of grid flexibility services focused on catering the evolving electricity grid challenges. Due to widespread adoption of utility scale renewable energy resources followed by national and regional regulations, significant growth in VPP and DERM is being observed in Europe particularly Germany and the UK. Furthermore, the UK and Germany are expected to remain the market leader in Europe with grid flexibility capacity projected to reach 45 GW in the UK and 80 GW in Germany in 2030.
On the other hand, PTR believes that owing to high energy consumption and solar generation per capita Australia is a prime location for VPPs. It is noteworthy that stakeholders in the country are showing strong affinity towards utilizing rooftop solar and residential storage capacity for advanced VPP platforms that have the ability to predict and manage grid congestion. Grid flexibility capacity of Australia is estimated to stand at around 1 GW in 2021 and it is expected to reach 16 GW in 2030.
To conclude, the electricity market structure of countries paves way for the development of grid flexibility market. In the absence of a suitable electricity market structure such technological solutions cannot be deployed, and widespread market participation of consumers cannot be ensured.